Integrative circRNA Solutions
CD Genomics is devoted to partnering with you to determine the optimal solution or technology to suit your specific circRNA research project. We provide advanced, flexible, scalable, and affordable solutions utilizing mass spectrometry (MS) or next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology to help scientists deepen the understanding of circRNA biology.
Overview of circRNAs
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) represent a class of non-coding RNAs with the 3' and 5' ends covalently linked. They are generally produced by alternative splicing of pre-mRNA, in which a downstream splice donor is joined to an upstream splice receptor in a process known as "backsplicing". Some studies have found that circRNAs are expressed in diverse eukaryotic organisms and are conservative across mammals. Most circRNAs consist of a single exon or multiple exons and have tissue-specific expression patterns. circRNAs were once considered to be "junk" except the testis-specific circRNA from the sex-determining region Y. In recent years, the advent of next-generation sequencing and circRNA-specific bioinformatics algorithms enables the discovery of thousands of circRNAs in eukaryotes and further prediction of circRNA function and underlying mechanisms. Many circRNAs are found to exert important biological functions by acting as microRNA (miRNA) sponges, by regulating protein function or by being translated themselves in a cap-independent manner. RNA-seq has revealed dysregulation of many circRNAs in various diseases such as neurological disorders and cancer, suggesting their engagement in disease development and progression and their potential as biomarkers.
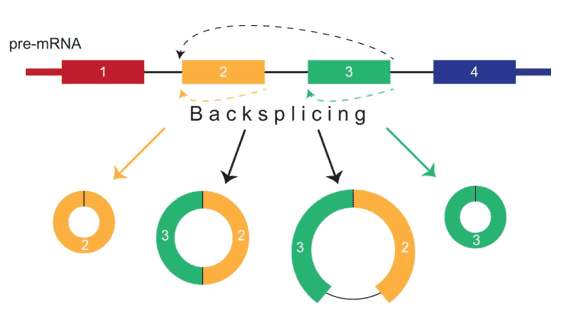 Figure 1. circRNA splicing and isoform diversity (Barrett and Salzman 2016).
Figure 1. circRNA splicing and isoform diversity (Barrett and Salzman 2016).
Characteristics of circRNAs
- Most circRNAs are found in the cytoplasm and are highly conservative in sequence.
- circRNAs are generally stable and the half lives are 48h, while mRNA has 10h half lives.
- circRNAs may show differential expression patterns across cells.
- circRNA are formed by alternative splicing of pre-mRNA and some can be translated.
- circRNAs can function as miRNA sponges and affect transcription and translation.
Our Solutions for Comprehensive circRNA Research
We provide a wide range of mass spectrometry (MS) and NGS approaches to help you achieve the following research purposes.
circRNA-miRNA Interaction Analysis
We provide RNA sequencing, circRNA sequencing and CLIP-seq to discover circRNA-miRNA interactions and reveal the regulatory networks involving miRNAs and circRNAs.
circRNA-Protein Interaction Prediction
We offer in vitro and in vivo experiments coupled with NGS or MS to detect circRNA-protein interactions. Our solutions include CLIP-seq, RIP-seq, ChIRP-seq, ChIRP-MS.
circRNA Modification Analysis
m6A is an abundant modification present on circRNA. We provide NGS-based approaches such as MeRIP-seq to comprehensively detect circRNA m6A modifications.
References:
- Barrett S P, Salzman J. Circular RNAs: analysis, expression and potential functions. Development, 2016, 143(11): 1838-1847.
- Kristensen L S, Andersen M S, Stagsted L V W, et al. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nature Reviews Genetics, 2019, 20(11): 675-691.
- Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavač M, Glavač D. Circular RNAs: biogenesis, function, and a role as possible cancer biomarkers[J]. International journal of genomics, 2017, 2017.